EAR SURGERIES
Know the Middle Ear
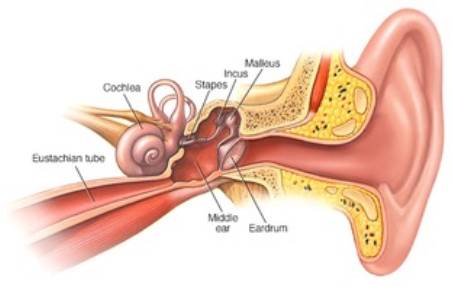
The middle ear has three sound conducting bones (called Ossicles) which transmit vibrations of the ear drum to the inner ear (cochlea). The cochlea converts the vibrations into electrical signals which are transmitted to the hearing centre in the brain. The signals reaching the hearing centre are perceived as sound.
The middle ear is an air containing space. Middle ear ventilation required for efficient sound transmission & is provided by the Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the nasal passages.
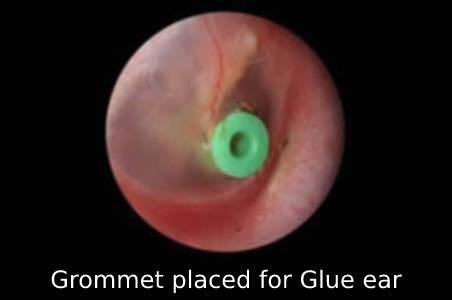
Placement of Tube
Glue ear is a condition wherein fluid or thick mucus accumulates in the middle ear.
A glue ear can result in conductive hearing loss. Being a common condition in the Paediatric age group, Glue ear can result in learning disabilities.
If conservative treatment with medicines fails, a minor surgery called Myringotomy is done. In this procedure the fluid in the middle ear is sucked out after incising the ear drum. A tube is placed across the incised site for improving middle ear ventilation.
Attention is given to the nose for any predisposing conditions. The predisposing condition may be nasal obstruction due to Deviated Nasal Septum, Adenoid enlargement (especially in children), Nasal Polyps & Sinus conditions.
Reconstruction of the middle ear & ear drum (Tympanoplasty)
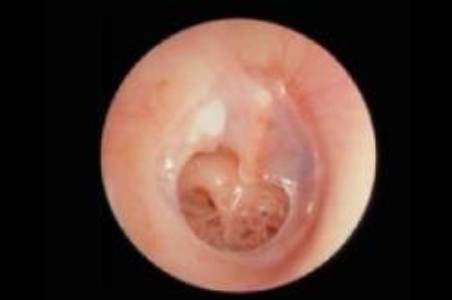
Chronic Otitis Media is a condition where the middle ear conducting system is damaged due to infection. The damage may be in the form of a perforation of the ear drum. This predisposes to recurrent discharge & some degree of hearing impairment. The perforated ear drum may be grafted to improve hearing & also prevent ear discharge.
Mastoidectomy with Tympanoplasty
Chronic Otitis Media may be due to growth of skin into the middle ear, a condition called cholesteatoma.
Cholesteatoma has the property of expansion thereby invading vital neighbouring structures resulting in complications like dizziness, Facial weakness & brain infection. This makes it mandatory for surgery to remove Cholesteatoma. Surgery involves drilling the bone in the vicinity of the middle ear (Mastoidectomy) to remove cholesteatoma. The ear drum & the middle ear are reconstructed in the same sitting
(Tympanoplasty)
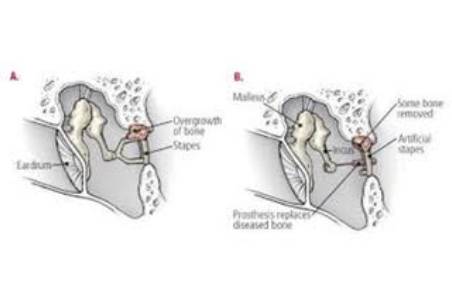
Stapedectomy for hearing Restoration
Otosclerosis is a familiar condition leading to progressive hearing loss. It is common in women with hearing loss starting in early adulthood. The hearing loss is due to bone remodelling resulting in fixation of the Stapes (the Stapes being the third bone of the middle ear).
Audiometry tests helps in identifying patients suitable for surgery. Hearing aid always remains an option if the patient declines surgery.
The surgical procedure to restore hearing in Otosclerosis is called Stapedectomy. The middle ear is entered & the fixed Stapes removed. An Implant is precisely placed to restore continuity of the middle ear sound conduction.